数据结构_单链表(C++
数据结构_SinglyLinkedList单链表(C++实现
前言:此类笔记仅用于个人复习,内容主要在于记录和体现个人理解,详细还请结合bite课件、录播、板书和代码。
[toc]
前言&注意事项
单链表C++的实现分为了结点类和链表类两个类,十分明了,可读性很高,也很容易写,节点类负责单个节点的操作,链表负责链表整体的操作
==assert果然还是太暴力了,能不用就不用吧,但是一定要记住要判断 表指针 为空的情况==
- ==可以抛出异常信号 (建议用这个,因为运行错误的时候知道原因==
- ==可以直接返回==
- 判断指针head为空的方式
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// head为空的话head就相当于0(假),非空就是真,所以当head为空的时候,!head就是真
throw nullPointer();//这里使用了抛出异常信号的方式,而且抛出的是一个匿名对象(因为要的是它的类型,没必要给对象命名了)
//如果采用直接返回的方式
if(!head)
return;//直接返回的话,在有返回类型的函数里面可能会报错
//以上两者都可以终止函数,不过直接return只能用在无返回值函数上,return本质是终止函数运行并返回NULL
实现
SList.h
c++
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
using namespace std;
class nullPointer
{
};//用作异常信号的类,遇到空指针时抛出,用于判断是否成功扩容以及头指针是否为空
class outofBound
{
}; //用作异常信号的类,用于判断是否越界cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
class sList; //类的向前说明,因为下面的node类将sList看作友元类,在此提前声明一下sList类的存在
//前面要声明参数模板,类后面不用跟参数模板
template <class elemType>
class node //节点类
{
friend class sList<elemType>;//之后的sList中要用到node的私有成员data和next,只有将sList看作了友元类才行在sList中(属于node类外)访问node的私有成员
//友元类后面一定要跟参数模板
private:
elemType data;
node *next;
public:
node() : next(NULL) {} //默认构造函数
node(const elemType &e, node *N = NULL) //含缺省参数的构造函数
{
data = e;
next = N;
}
};==这里一定要注意为什么提前声明sList以及为什么node类将sList类看作友元类==
==还要注意==
==类的向前声明的时候类后面不加模板参数,但是前面一定要有参数模板的声明;==
==友元类后面一定要有模板参数==
==就按上面的写法==
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
class sList //单链表类
{
private:
node<elemType> *head;
public:
sList(); //构造函数,建立一个空链表
bool sListempty() const; //判空,空则返回真,否则返回假
// bool sListFull()const;//判满(额,我倒是想知道怎么判断是满的,没什么用这个
int sListLength() const; //返回链表长度
void sListPushBack(elemType &e); //尾插
void sListPushHead(elemType &e); //头插
void sListPopBack(); //尾删
void sListPopHead(); //头删
void sListInsert(int pos, elemType &e); //在pos位置插入e(在pos结点的前面插入e
void sListErase(int pos); //删除pos结点
elemType sListGet(int pos); //返回pos处的节点的值
int sListFind(elemType &e); //返回值等于e的结点的序号,没有匹配的则返回0
void sListRemove(int pos, elemType &e); //移除pos处的数据并赋值给e
void sListReverse() const; //单链表元素就地逆置
void sListClear(); //清空单链表,保留head结点,释放其余空间
~sList(); //析构函数,销毁单链表,释放所有空间
};SList.cpp
包含头文件以及构造函数的定义
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
template <class elemType>
sList<elemType>::sList() //构造函数,建立一个空链表
{
head = new node<elemType>(); //开辟一个结点对象空间(这里new的对象最后面这里加了括号,加不加括号的区别请看code日记)
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
bool sList<elemType>::sListempty() const //判空,空则返回真,否则返回假
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
return head->next == NULL;
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
int sList<elemType>::sListLength() const //返回链表长度
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
int size = 0;
node<elemType> *p = head->next; //这里是让p=head->next这样可以统计有效节点的个数
while (p)
{
size++;
p = p->next;
}
return size;
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
void sList<elemType>::sListPushBack(elemType &e) //尾插
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
node<elemType> *New, *p = head; //这里让p=head,因为有链表为空的情况
New = new node<elemType>(e); //new了一个data初始化了的对象
while (p->next) //找到最后一个节点
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = New;
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
void sList<elemType>::sListPushHead(elemType &e) //头插
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
node<elemType> *New, *p = head->next;
New = new node<elemType>(e);
head->next = New;
New->next = p;
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
void sList<elemType>::sListPopBack() //尾删
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
node<elemType> *p = head;
if (head->next == NULL) //如果链表是空的
return; //直接返回上一级函数
if (head->next->next == NULL) //如果只有一个有效节点,不用找尾
{
delete head->next;
head->next = NULL;
}
else
{
while (p->next->next) //找尾
{
p = p->next;
}
delete p->next;
p->next = NULL;
}
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
void sList<elemType>::sListPopHead() //头删
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
node<elemType> *p = head->next;
if (head->next == NULL) //如果链表是空的
return; //直接返回上一级函数
else
{
head->next = p->next;
delete p;
}
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
void sList<elemType>::sListInsert(int pos, elemType &e) //在pos位置插入e(在pos节点的前面插入e
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
if (pos < 1) //如果pos小于1则非法访问(越界
throw outofBound();
node<elemType> *p = head, *New;
int j = 0;
while (p && j < pos - 1) // p为空说明走到了链表的最后面,也就是NULL
{
j++;
p = p->next;
}
if (!p)
throw outofBound();
// return;
New = new node<elemType>(e, p->next);
p->next = New;
} p的位置是在pos位的前一个,数据插在pos的位置就是插在p的后面,如果p在尾节点,插入在p的后面是没问题的,如果p走到了节点的尾部也就是尾结点的next也就是NULL,那说明pos肯定是超出了范围,否则在此之间p就能走到pos的前一个位置而终止循环
插入是可以尾插的,即pos的位置是在最后一个节点的后面,或者说NULL的前面,此时p在尾结点
while里面j的作用是判断有没有走到pos的位置之前,如果j=pos-1,说明p走到了pos的前一个位置
如果数组长度为7,pos的位置是8,那么在p走到最后一个节点的时候,j=7,p就停止移动,此时相当于尾插
如果数组的长度是7,pos的位置是9,那么在p走到最后一个节点的时候,j=7,p不为空,j<8,p继续后移到NULL,此时走了到链表的尽头,说明了链表长度不够,要插入的位置是在NULL还往后,这是非法访问
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
void sList<elemType>::sListErase(int pos) //删除pos节点
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
if (pos < 1)
throw outofBound();
node<elemType> *p = head;
int j = 0;
while (p->next && j < pos - 1) // p->next为空说明p走到了最后一个节点,如果走到了最后一个节点,说明pos的位置越界
{
j++;
p = p->next;
}
if (!p->next)
throw outofBound();
node<elemType> *tmp = p->next; // p是pos的前一个节点
p->next = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
}删除只能删除存在的节点,如果删除超过长度的节点就是非法的,所以pos只能访问存在的节点的位置,即在NULL之前,head之后
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
elemType sList<elemType>::sListGet(int pos) //返回pos处的节点的值
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
if (pos < 1)
throw outofBound();
int j = 0;
node<elemType> *p = head;
while (p->next && j < pos - 1)
{
j++;
p = p->next;
}
if (!p->next)
throw outofBound();
return p->next->data;
}也是只能访问存在的节点的位置
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
int sList<elemType>::sListFind(elemType &e) //返回值等于e的结点的序号,没有匹配的则返回0
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
int i = 1;
node<elemType> *p = head->next;
while (p)
{
if (p->data == e)
return i;
i++;
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
void sList<elemType>::sListRemove(int pos, elemType &e) //移除pos处的数据并赋值给e
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
if (pos < 1)
throw outofBound();
node<elemType> *p = head;
int j = 0;
while (p->next && j < pos - 1)
{
j++;
p = p->next;
}
if (!p->next)
return;
node<elemType> *tmp = p->next; // p是pos的前一个节点
p->next = tmp->next;
e = tmp->data; //将pos出的data赋值给引用e
delete tmp;
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
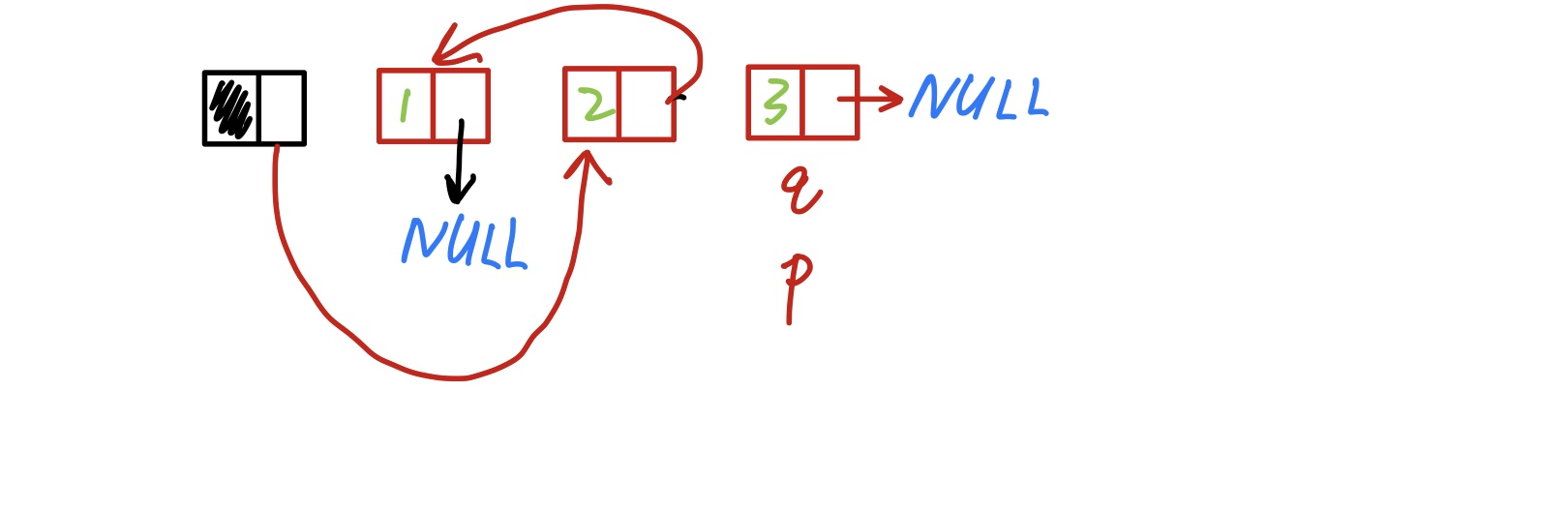
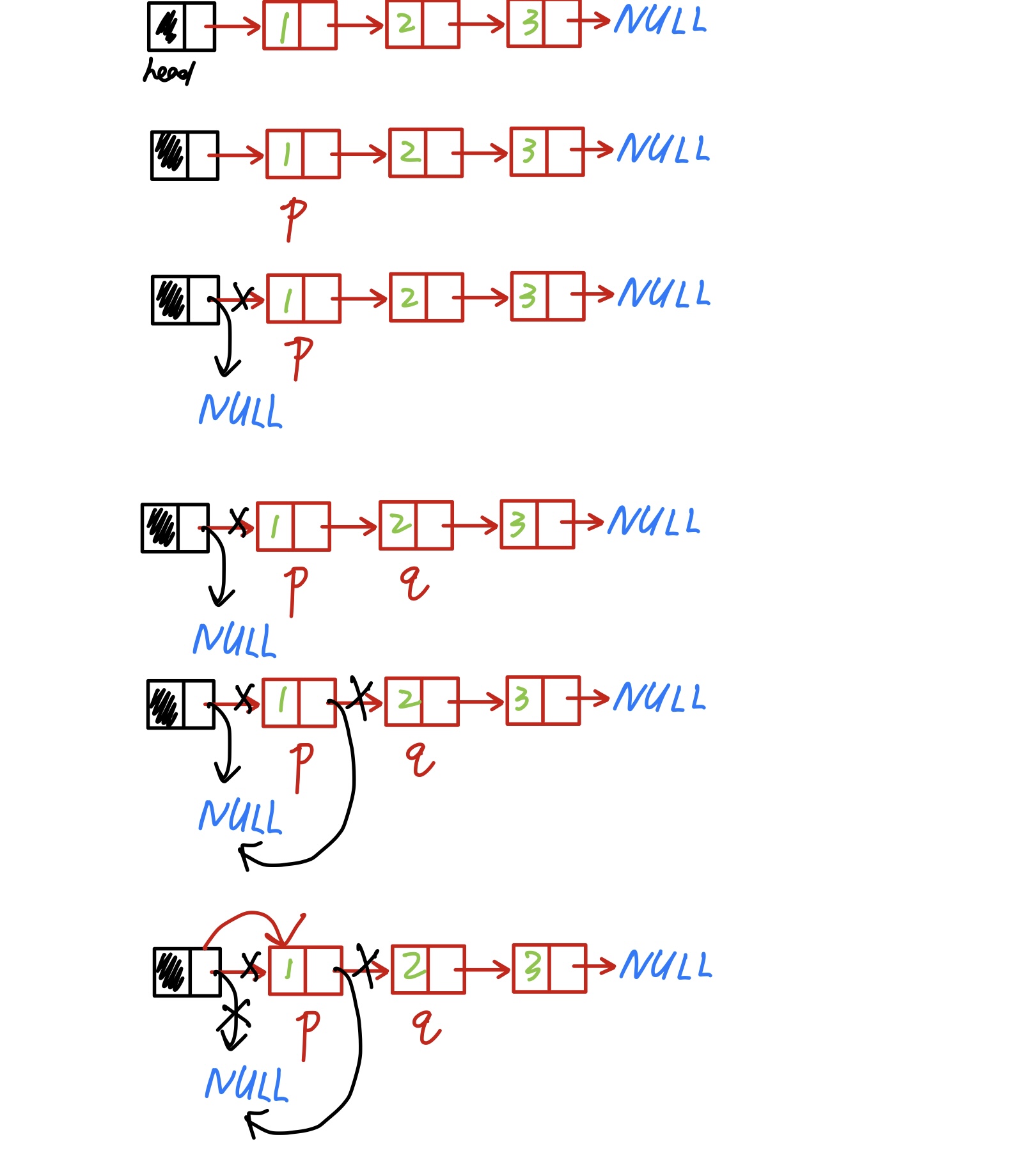
void sList<elemType>::sListReverse() const //单链表元素就地逆置 (这个比较重点
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
node<elemType> *p, *q; //兄弟协同
p = head->next;
head->next = NULL;
while (p)
{
q = p->next;
p->next = head->next;
head->next = p; //首席插入
p = q;
}
}
 cpp
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
void sList<elemType>::sListClear() //清空单链表,保留head结点,释放其余空间
{
if(!head)
throw nullPointer();
node<elemType> *p = head->next;
while (p)
{
head->next = p->next;
delete p;
p = head->next;
}
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
sList<elemType>::~sList() //析构函数,销毁单链表,释放所有空间
{
sListClear();
delete head;
head == NULL;
}
总结
- 头部操作比尾部操作简单,因为尾部操作需要先找尾,找尾还要看有效节点是一个还是多个,一个的话就不用找,多个的话就要找
- 这里我犯了一个糊涂,混淆了一些东西,解释一下:
- new开辟动态内存之后返回的是地址
- 访问对象的成员的时候的格式是 对象.成员 ;使用指针来访问对象成员的时候是 对象指针->成员
这一点是因为,类和对象是一种特殊的结构体(自定义类型),结构体访问成员就是
结构体名.结构体成员
或者
结构体指针->结构体成员
- 匿名对象名后面无论加不加初始化参数都要有括号(C++异常处理有说明)
- 一定要写对单词!我写顺序表因为main写成mian找了很长时间的错误,写单链表因为friend写成了frind又找了很久错误
练习
1.约瑟夫环
n个人围成一个圈,从1、2、3开始报数。当报到m时,第m个人出列,并从原来的第m+1人重新开始1、2、3报数。如此循环,直到圈中只剩下一个人。这个圈称为约瑟夫环。试用单向循环链表实现该游戏,并输出最后剩下的那人的姓名。
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
using namespace std;
struct Node//单链表结点
{
Node* next;
string name;
};
struct Ring//约瑟夫环结构体(单向循环链表)
{
Node* head;
Node* tail;
};
void ThrowOut(Ring* ring, int n, int m)//用于让第m个人出列
{
if (n < m)
return;
int j = 1;
Node* temp=ring->head;
Node* x=NULL;
for (j; j < m-1; j++)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
//cout << temp->next->name << endl;//输出每次出列的人的名字
x = temp->next;
temp->next = temp->next->next;
free(x);
ring->tail = temp;
ring->head = temp->next;
}
void ringGame(Ring* ring,int n)//约瑟夫环游戏实现函数
{
while (ring->head == ring->tail)
{
int m;
cout << "Please keynode the number you want to throw out" << endl;
cin >> m;
ThrowOut(ring, n, m);
}
cout <<"The last member's name is: "<< ring->head->name << endl;
}2.已知表头元素为c的单链表在内存中的存储状态如下表所示
地址 1000H a 1010H 1004H b 100CH 1008H c 1000H 100CH d NULL 1010H e 1004H 1014H 现将f存放于1014H处并插入到单链表中,若f在逻辑上位于a和e之间,则a,e,f的“链接地址”依次是什么?
原来逻辑上:c,a,e,b,d
现在逻辑上:c,a,f,e,b,d
则a的链接地址(后继指针)变成了f的地址,f的链接地址变成了e的,e的不变
即a->next=1014H, f->next=1010H, e->next=1004H
3.集合的并、差(不一定是有序的集合
利用链式结构分别实现集合运算
$$
C=A\cup B、C=A-B=A-A\cap B
$$
并分析其时间复杂度。要求运算结束后在内存中的A、B两个集合中的元素不变思路:
求并集的时候,可以先将A、B简单相加得C,然后删除C中数据重复的结点
求差时候,以A为基础,A中的每个结点和B比较,A、B中有相同的就不插入C,把A中具有且B中没有的插入到C
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
using namespace std;
struct Node//单链表结点
{
Node* next;
int data;//方便起见就假设集合是一个数集吧~~
};
class CT//集合结构体,CT是collection的缩写
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
CT();
void And(CT*, CT*);
void Difference(CT*, CT*);
};
CT::CT()
{
Node* C = new Node();
head = C;
C->next = NULL;
C->data = 0;
}
void CT::And(CT* A, CT* B)//求并集:A+B-AB
{
if (A == NULL || B == NULL )
return;
Node* a = A->head;
Node* b = B->head;
Node* c = head;
while (a)
{
c->data = a->data;
c->next = new Node();
c = c->next;
c->next = NULL;
a = a->next;
}
while (b)
{
c->data = b->data;
c->next = new Node();
c = c->next;
c->next = NULL;
b = b->next;
}
c = head;
while (c)
{
Node* x = c;
Node* y = c->next;
while (y)
{
if (c->data != y->data)
{
x = x->next;
y = y->next;
}
else
{
x->next = y->next;
delete(y);
y = x->next;
}
}
c = c->next;
}
}
void CT::Difference(CT* A, CT* B)//求差集,遍历A中的每一个元素的时候遍历B中的每一个元素,有相同的就不加入到C,没有就加入到C
{
Node* a = A->head;
Node* c = head;
if (A == NULL || B == NULL)
return;
while (a)
{
Node* b = B->head;
while (b)
{
if (a->data == b->data)
{
break;
}
else
{
b = b->next;
}
}
if (b == NULL)
{
c->data = a->data;
c->next = new Node();
c = c->next;
c->next = NULL;
}
a = a->next;
}
}
题目
==下面这些函数都是直接在上面👆写好的单链表头文件(sList.h)中作为了成员函数声明的,并在另一个文件中定义的==
当然也可以不用作为成员函数,而是重新写一个头文件和源文件,并在头文件中包含单链表的源文件来使用写好的单链表
但是因为题目大都是在现有链表的基础上进行操作,也就是对链表进行操作,不如直接写成链表的成员函数,直接在链表中调用更方便
1.求两个递增单链表的交、并、差集,并且要求结果也是递增的单链表
请用两种方案实现:一种是用原有空间,一种是用新的空间
用原有空间的话,就是以A为主链,将A作为结果
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
template<class elemType>
void sList<elemType>::intersection(sList& b)
{
node<elemType> *i, *j;
i = head;
j = b.head->next;//这里有个彩蛋,类内访问外部同类对象的私有成员,这是合理的
while (i->next && j)
{
if (i->next->data == j->data)
{
i = i->next;
j = j->next;
}
else
{
if (i->next->data < j->data)
{
node<elemType> *k = i->next;
i->next = i->next->next;
delete (k);
k = NULL;
}
else
j = j->next;
}
}
while (i->next)//如果主集合i指针之后不会空,应该清除多余的元素
{
node<elemType> *k = i->next;
i->next = i->next->next;
delete (k);
k = NULL;
}
cout << "交集是" << endl;
for (int x = 1; x <= sListLength(); x++)
{
cout << sListGet(x) << " ";
}
if (sListLength() == 0)
cout << "空集" << endl;
cout << endl;
}
//这里要注意,因为涉及删除,所以a中要用两个指针,或者指针指向被判断的元素的前一个,指针的next指向被判断的元素,为删除做准备cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
template<class elemType>
void sList<elemType>::unionSet(sList& b)
{
node<elemType> *i, *j;
i = head;
j = b.head->next;
while (i->next && j)
{
if (i->next->data == j->data)
{
i = i->next;
j = j->next;
}
else
{
if (i->data < j->data)
{
if (i->next->data > j->data)
{
node<elemType> *k = new node<elemType>;//这里要注意,如果只是将j的结点给i的next,则结点之后所有都是j的结点了,因此只能新开一个结点并赋值
k->next = i->next;
k->data = j->data;
i->next = k;
}
else
i = i->next;
}
else
j = j->next;
}
}
if (j)//如果b没有走完,b中剩下的的元素一定都是比a中的大的,因此不用判断大小,全部给到a就可以,而且直接连接上结点就可以,不用新开结点再赋值
{
i->next = j;
}
cout << "并集是" << endl;
for (int x = 1; x <= sListLength(); x++)
{
cout << sListGet(x) << " ";
}
if (sListLength() == 0)
cout << "空集" << endl;
cout << endl;
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
template<class elemType>
void sList<elemType>::complementarySet(sList& b)
{
node<elemType> *i, *j;
i = head;
j = b.head->next;
while (i->next && j)
{
if (i->next->data == j->data)
{
node<elemType> *k = i->next;
i->next = i->next->next;
delete (k);
k = NULL;
j = j->next;
}
else
{
if (i->next->data < j->data)
{
i = i->next;
}
else
{
j = j->next;
}
}
}
cout << "差集是" << endl;
for (int x = 1; x <= sListLength(); x++)
{
cout << sListGet(x) << " ";
}
if (sListLength() == 0)
cout << "空集" << endl;
cout << endl;
}用申请新空间的方案:也就是用另外一个链表C作为结果链
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
template<class elemType>
void sList<elemType>::intersection_new(sList& a, sList& b)
{
node<int> *i = a.head->next;
node<int> *j = b.head->next;
while (i && j)
{
if (i->data == j->data)
{
sListPushBack(i->data);
i = i->next;
j = j->next;
}
else
{
if (i->data < j->data)
i = i->next;
else
j = j->next;
}
}
cout << "交集是" << endl;
for (int x = 1; x <= sListLength(); x++)
{
cout << sListGet(x) << " ";
}
if (sListLength() == 0)
cout << "空集" << endl;
cout << endl;
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
template<class elemType>
void sList<elemType>::unionSet_new(sList& a, sList& b)
{
node<int> *i = a.head->next;
node<int> *j = b.head->next;
while (i && j)
{
if (i->data == j->data)
{
sListPushBack(i->data);
i = i->next;
j = j->next;
}
else
{
if (i->data < j->data)
{
sListPushBack(i->data);
i = i->next;
}
else
{
sListPushBack(j->data);
j = j->next;
}
}
}
while (i)
{
sListPushBack(i->data);
i = i->next;
}
while (j)
{
sListPushBack(j->data);
j = j->next;
}
cout << "并集是" << endl;
for (int x = 1; x <= sListLength(); x++)
{
cout << sListGet(x) << " ";
}
if (sListLength() == 0)
cout << "空集" << endl;
cout << endl;
}cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
template<class elemType>
void sList<elemType>::complementarySet_new(sList& a, sList& b)
{
sList<int> K;//先求出ab的交集K
node<int> *m = a.head->next;
node<int> *n = b.head->next;
while (m && n)
{
if (m->data == n->data)
{
K.sListPushBack(m->data);
m = m->next;
n = n->next;
}
else
{
if (m->data < n->data)
m = m->next;
else
n = n->next;
}
}
node<int> *k = K.head->next;
node<int> *i = a.head->next;
while (i && k)
{
if (i->data != k->data)
{
sListPushBack(i->data);
i = i->next;
}
else
{
i = i->next;
k = k->next;
}
}
while (i)
{
sListPushBack(i->data);
i = i->next;
}
cout << "差集是" << endl;
for (int x = 1; x <= sListLength(); x++)
{
cout << sListGet(x) << " ";
}
if (sListLength() == 0)
cout << "空集" << endl;
cout << endl;
}
2.已知线性表中的元素以值递增有序排列,并以单链表做存书结构。请写一种高效的算法,删除表中所有值大于mink且小于maxk的元素(如果表中有这样的元素),同时释放被删除的结点空间,并分析一下算法的时间复杂度
用双指针就可以解决,一个i在前,一个j在后
i先找到区间(大于mink小于maxk的区间)之前的第一个元素(也就是小于mink的元素里面的最后一个元素)(此时i->data<=mink , i->next->data>=mink)
然后j开始往后找到区间之后的第一个元素(也就是j一直往后,直到j->data>=mark)
cpp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
void sList<elemType>::interval(int mink, int maxk)
{
node<int> *i, *j;
j = i = head->next;
while (i->next)
{
if (i->data <= mink && i->next->data <= mink)
i = i->next;
else
break;
}
j = i;
while (j->next)
{
if (j->data < maxk )
j = j->next;
else
break;
}
while (i->next != j)
{
node<int> *k = i->next;
i->next = i->next->next;
delete k;
k = NULL;
}
}
结束
That’s all, thanks for reading!💐

.PNG)