2022.10.10智慧树作业_栈和队列 [toc]
第一题 相同点:
在逻辑上都是线性结构,栈和队列本质就是特殊的线性表,都可以用链表或者顺序表进行存储
不同点:
栈、队列具有特定的性质,特定的运算规则
第二题 1 2 3 4 5、1 2 3 5 4、1 2 4 3 5、1 2 4 5 3、1 2 5 4 3、1 3 2 4 5、1 3 2 5 4、1 3 4 2 5、1 3 4 5 2、1 3 5 4 2、1 4 3 2 5、1 4 3 5 2、1 4 5 3 2、1 5 4 3 2、2 1 3 4 5、2 1 3 5 4、2 1 4 3 5、2 1 4 5 3、2 1 5 4 3、2 3 1 4 5、2 3 1 5 4、2 3 4 1 5、2 3 4 5 1、2 3 5 4 1、2 4 3 1 5、2 4 3 5 1、2 4 5 3 1、2 5 4 3 1、3 2 1 4 5、3 2 1 5 4、3 2 4 1 5、3 2 4 5 1、3 2 5 4 1、3 4 2 1 5、3 4 2 5 1、3 4 5 2 1、3 5 4 2 1、4 3 2 1 5、4 3 2 5 1、4 3 5 2 1、4 5 3 2 1、5 4 3 2 1
第三题 现有一个元素均为整数的栈,使用另一个临时栈对其进行非递减排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 template <class elemType >void seqStack<elemType>::sort (){ seqStack tmp; for (int k = Top; k > -1 ; k--) { int K = top (); pop (); if (tmp.isEmpty ()) { tmp.push (K); } else { while (!tmp.isEmpty ()) { if (K <= tmp.top ()) { push (tmp.top ()); tmp.pop (); } else break ; } tmp.push (K); int q = Top; while (q >= k) { tmp.push (top ()); pop (); q--; } } } while (!tmp.isEmpty ()) { push (tmp.top ()); tmp.pop (); } }
要求对栈进行非递减排序,就是栈底最大,栈顶最小
思路就是把主栈元素依次出到临时栈来进行排序,在临时栈中排成栈底最小,栈顶最大
主栈栈顶大于等于临时栈顶,直接出主栈入临时栈
小于临时栈顶,主栈栈顶先出栈赋值给k,临时栈逐个出栈到主栈,直到临时栈顶小于k,k入临时栈,在将之前放到主栈的临时栈元素放回临时栈
第四题 设计算法判别表达式中的括号是否配对出现, 平衡的表达式中’{‘、’}’,’(‘、’)’,’[‘、’]’ 应成对按序出现。
例如”{[()]{()}{()() }}” 是括号匹配的表达式, 而”[({}])”是括号不匹配的表达式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 template <class elemType >int seqStack<elemType>::parentheses (string s){ int size = s.length (); for (int x = 0 ; x < size; x++) { if (s[x] == '(' || s[x] == '{' || s[x] == '[' ) { push (s[x]); } else if (s[x] == ')' || s[x] == '}' || s[x] == ']' ) { if (s[x] == ')' && top () == '(' ) pop (); else if (s[x] == '}' && top () == '{' ) pop (); else if (s[x] == ']' && top () == '[' ) pop (); else return -1 ; } } if (!isEmpty ()) return -1 ; return 0 ; }
第五题 用两个栈实现队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 template <class elemType >class Queue_stack { private : seqStack<elemType> a, b; public : void push (const elemType &x) { b.push (x); } void pop () { if (a.isEmpty ()) while (!b.isEmpty ()) { a.push (b.top ()); b.pop (); } a.pop (); } elemType top () { if (a.isEmpty ()) while (!b.isEmpty ()) { a.push (b.top ()); b.pop (); } return a.top (); } void isEmpty () { return (a.isEmpty () && b.isEmpty ()); } };
原理:一个栈负责入队列,一个栈负责出队列,一旦出队列栈为空,就把入队列栈中所有元素都出到出队列栈
第六题 用两个队列实现栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include "queue.cpp" template <class elemType > int Queue<elemType>::size (){ Node<elemType> *p = head; int x = 0 ; while (p) { x++; p = p->next; } return x; } template <class elemType >class Stack_queue { private : Queue<elemType> a, b; public : void push (const elemType &x) { if (!a.isEmpty ()) a.pushQueue (x); else b.pushQueue (x); } void pop () { Queue<elemType> *qEmpty = a.isEmpty () ? &a : &b; Queue<elemType> *qUnEmpty = a.isEmpty () ? &b : &a; while (qUnEmpty->size () > 1 ) { qEmpty->pushQueue (qUnEmpty->getHead ()); qUnEmpty->popQueue (); } qUnEmpty->popQueue (); } elemType top () { Queue<elemType> *qEmpty = a.isEmpty () ? &a : &b; Queue<elemType> *qUnEmpty = a.isEmpty () ? &b : &a; while (qUnEmpty->size () > 1 ) { qEmpty->pushQueue (qUnEmpty->getHead ()); qUnEmpty->popQueue (); } int x = qUnEmpty->getHead (); qEmpty->pushQueue (qUnEmpty->getHead ()); qUnEmpty->popQueue (); return x; } };
两个队列,一个总是空的,一个总是不空的
入栈就进非空队列,出栈把非空队列的前n个出到空队列,pop非空队列最后一个元素
非空队列就变成了空队列,空队列就变成了非队列
第七题 现有一个整数队列, 需要将其前 k 个元素进行逆置, 剩余的元素保持原来的顺序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 template <class elemType >void Queue<elemType>::Reverse_k (int k){ Queue<elemType> q; seqStack<elemType> s; int i=0 ; while (i<k) { s.push (getHead ()); popQueue (); i++; } while (head) { q.pushQueue (getHead ()); popQueue (); } while (!s.isEmpty ()) { pushQueue (s.top ()); s.pop (); } while (q.head!=NULL ) { pushQueue (q.getHead ()); q.popQueue (); } }
思路:前k个元素放到临时栈,后n-k个元素放到临时队列,再从临时栈中入到主栈,临时队列入到主栈
第八题 给定一个整型的顺序表, 表示在同一行的行星。 对于其中的元素, 正负值代表其一维的移动方向, 可以理解为正数代表行星向右移动, 负数代表行星向左移动。 方向相同的行星不会碰撞, 如果两个行星相向而行则会相互碰撞, 则较小的行星(绝对值代表行星大小)会爆炸, 大小相同时两者都会爆炸。 请设计程序给出行星碰撞后的结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 template <class elemType >void seqStack<elemType>::planet (){ seqStack<int > s; while (!isEmpty ()) { if (s.isEmpty ()) { s.push (top ()); pop (); } else { if (s.top () < 0 ) { if (top () < 0 ) { s.push (top ()); pop (); } else { if (s.top () + top () > 0 ) s.pop (); else if (s.top () + top () < 0 ) pop (); else { s.pop (); pop (); } } } else { s.push (top ()); pop (); } } } while (!s.isEmpty ()) { push (s.top ()); s.pop (); } }
思路:(有点 类似中缀式转后缀式)
这个顺序表就是主栈,再创建一个临时栈
临时栈为空,主栈栈顶进临时栈;主栈栈顶是小于0的,进临时栈;主栈栈顶大于0,临时栈小于零,判断他俩的和,大于零说明主栈栈顶绝对值大,保留主栈栈顶,临时栈顶出栈,否则反之,如果和等0,则两边都出栈。最后主栈空了就临时栈出栈到主栈
因为结果保存在了栈里,输出的时候顺序是反的,不过只要再写一个逆置的函数就可以,比如把栈元素放到队列了,再出队列到栈就可以了
第九题 现在有一批同学需要接收面试, 参加面试的同学按照先到先面试的原则接受面试官的考查。 本次面试中面试官最看重的是同学的成绩, 现在面试官小明需要你设计程序实现以下功能:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 template <class elemType >class interview_team ; template <class elemType >class iNode { friend class interview_team <elemType>; private : string name; int point; iNode<elemType> *next; public : iNode (string name = "null" , int point = 0 ) { this ->name = name; this ->point = point; next = NULL ; } }; template <class elemType >class interview_team { private : iNode<elemType> *head, *tail; public : interview_team () { head = tail = NULL ; } void i_push (string name, int point) { if (head == NULL ) { head = tail = new iNode <elemType>(name, point); } else { tail->next = new iNode <elemType>(name, point); tail = tail->next; } } void i_pop () { if (head == NULL ) return ; iNode<elemType> *p = head; head = head->next; delete (p); if (head == NULL ) tail == NULL ; } int i_best () { if (!head) return -1 ; iNode<elemType> *p = head; int best = -1 ; while (p) { if (p->point > best) best = p->point; p = p->next; } return best; } };
思路:其实就是实现STL的队列中的部分功能
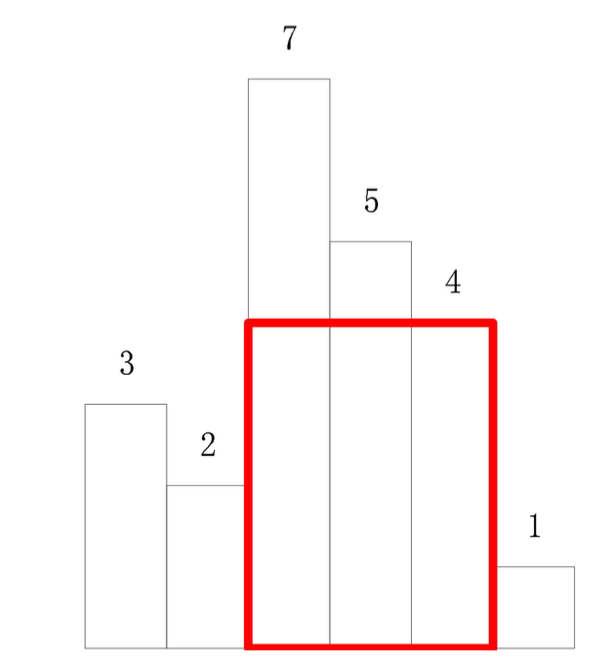
第十题 现有一个柱状图中,其中每个矩形柱子皆为相邻,且宽度相等,默认为 1,现在需要知道在这个柱形图中能够找到的最大矩形的面积。数据用一组非负的整数来表示,代表每根柱形的高度,请算出最大矩形的面积。
例如,已知每根柱形的宽度为 1,若给出的非负整数为[3,2,7,5,4,1]。图中的阴影部分为 最大矩形的面积,即 12 个单位的面积。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 int Rectangle (seqStack<int > now) seqStack<int > pass; seqStack<int > elem; int rectangle = 0 ; while (!now.isEmpty ()) { int d = now.top (); int p = 0 ; int n = 0 ; now.pop (); elem.push (d); while (!pass.isEmpty ()) { if (pass.top () >= d) { elem.push (pass.top ()); pass.pop (); p++; } else break ; } while (!now.isEmpty ()) { if (now.top () >= d) { elem.push (now.top ()); now.pop (); n++; } else break ; } int r = d * (1 + p + n); if (r > rectangle) rectangle = r; while (n > 0 ) { now.push (elem.top ()); elem.pop (); n--; } while (!elem.isEmpty ()) { pass.push (elem.top ()); elem.pop (); } } return rectangle; }
用栈
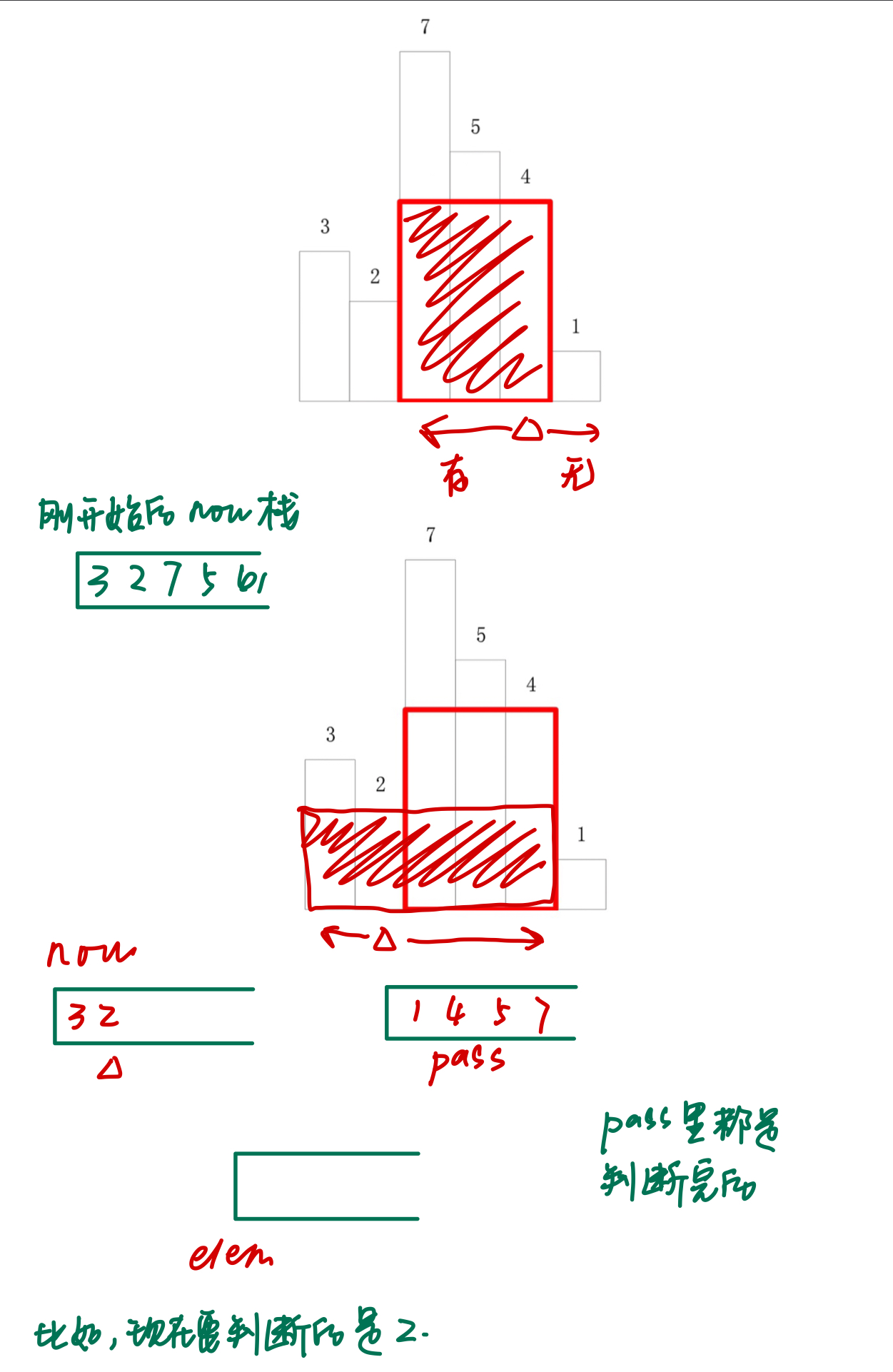
一个现在栈now(也是形参)
开两个临时站”临时站elem“、”过去栈pass“
如果判断一个元素能形成的矩形的面积,要往它的左右相邻看(不能中断),如果有左、右大于它,就能和左、右构成矩形,也就是这个矩形的高是这个元素,宽是构成矩形的元素的个数
元素是now栈的栈顶,pass栈里存放的是判断过的元素,也就是正在判断的元素的右面的元素,而正在判断的元素左边的元素就是now里的
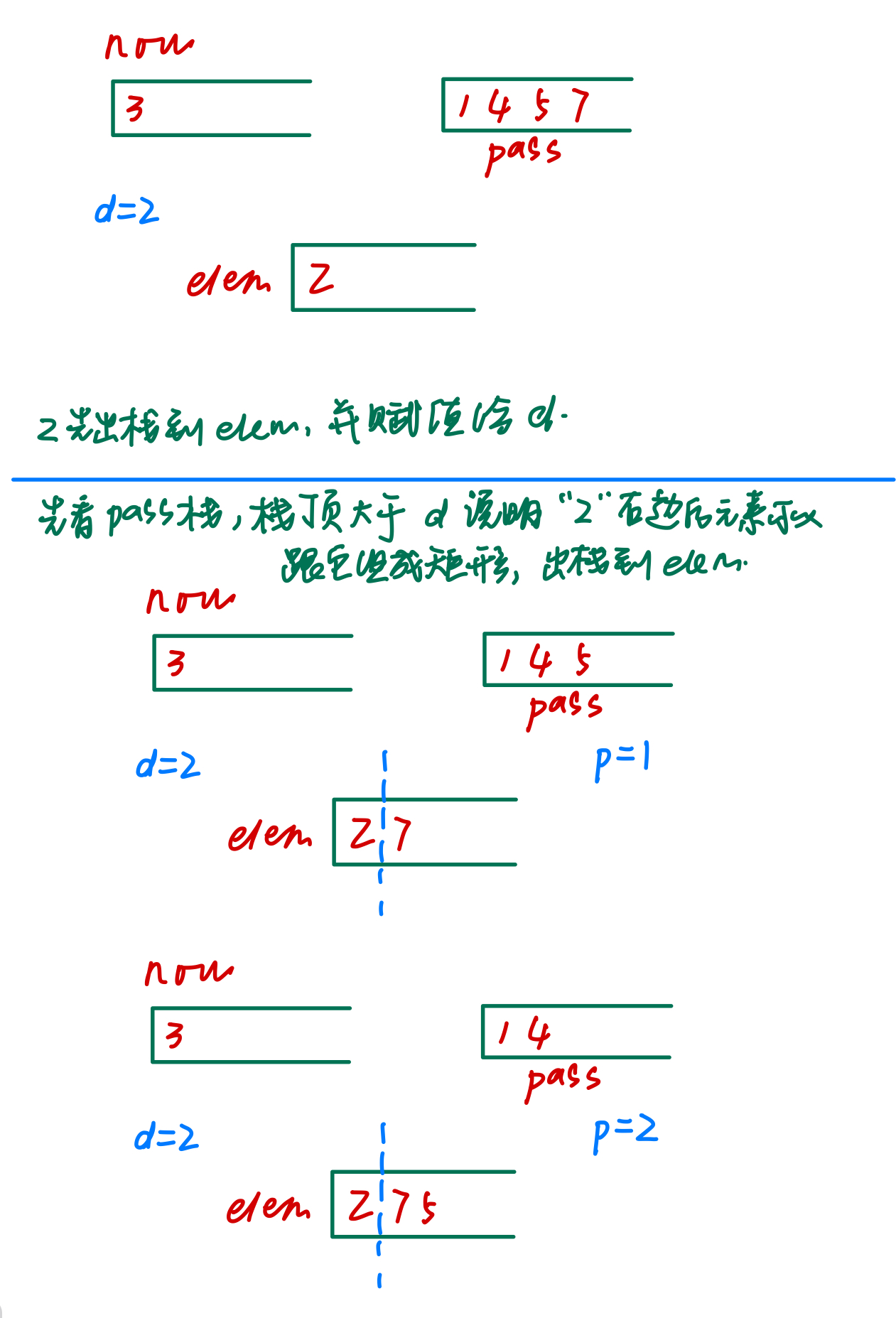
先将判断的元素出栈,赋值给d,并入栈到elem,elem是一个用来集合符合左右大于判断的元素的元素的栈,elem里的元素都是能构成矩形的元素
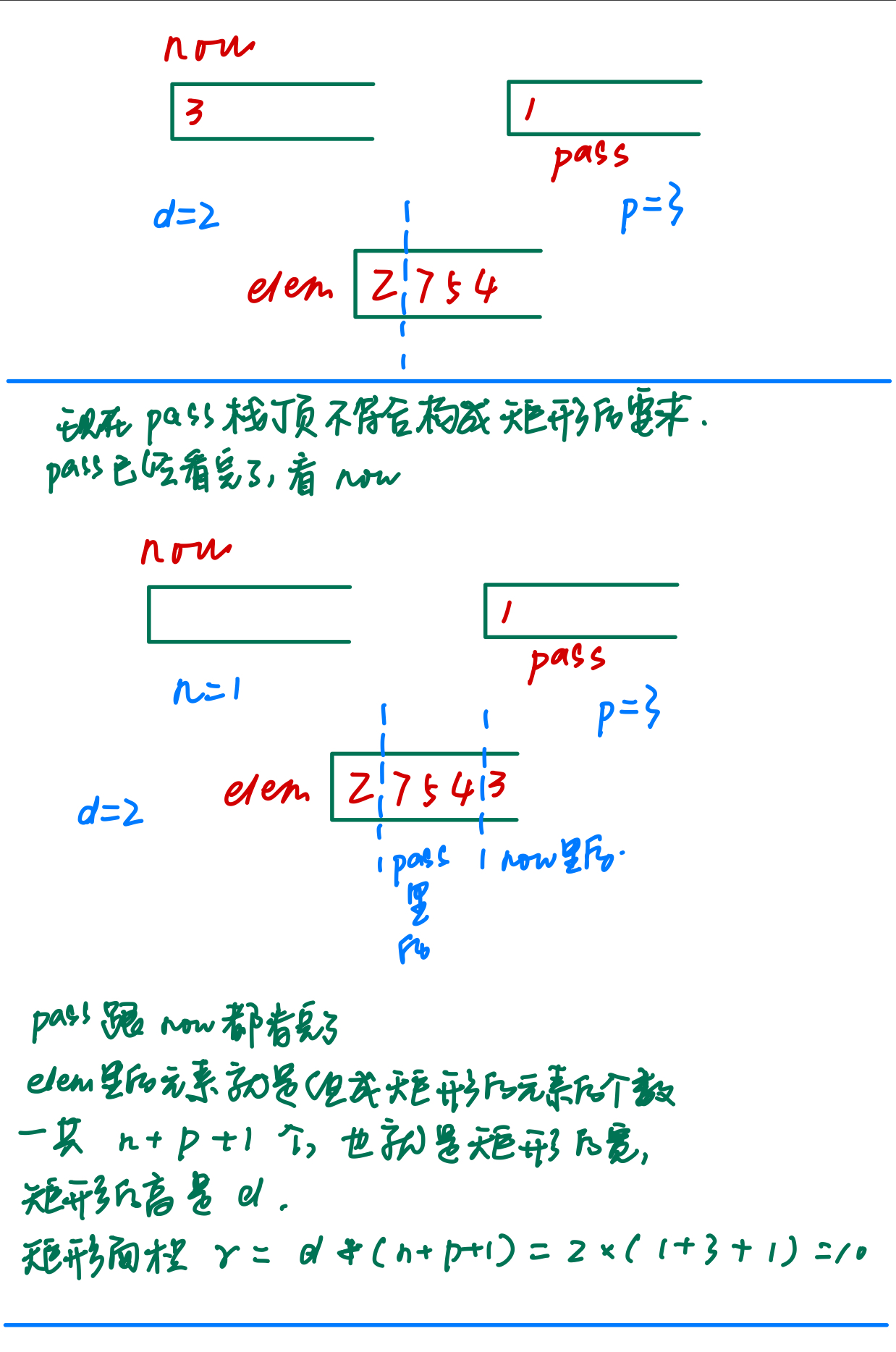
先判断 被判断的元素右面有没有可以和它组成矩形的元素,也就是从pass里找,如果栈顶大于,就出pass到elem中,再看pass的新栈顶,直到pass栈顶小于被判断的元素。pass每出一个元素到elem中,就用p计数,p++。p用来记录被判断的元素右面有几个可以和它组成矩形的元素。
再看 被判断的元素左面,也就是从now里找,因为被判断的元素已经出now了,所以现在now里是新栈顶,如果now栈顶大于被判断的元素,就出now到elem,再看新栈顶,直到now栈顶小于被判断的元素。用n计数出now到elem的元素个数。
现在就可以计算当前被判断的元素能组成的矩形面积了:高(d) * 宽(p+n+1),其中1是被判断的元素自己,p+n+1就是组成矩形的元素的个数,也就是elem里元素的个数
因为进elem的顺序是:
d、p个pass栈的、n个now栈的
而now、pass栈进了elem还得出来,因为elem只是起统计作用的,不能破坏原来now和pass的内容
因为elem的元素还要回到now和pass里
now最后进的,就先出,进了n个,就每次出一个,n–,直到n=0,说明elem里now的元素都返回now了
elem里剩下的全部进pass就可以,因为elem栈底的d刚刚被判断过了,应该属于pass了,即元素出elem到pass直到elem空